9-python关键方法
列表排序
两个长度一样的列表,一个是名称,一个是值,按照值的大小排序
| combined = zip(x,y)
x, y = zip(*sorted(combined, key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True))
|
过滤 filter()
| filter(function, iterable)
function 是一个函数,它的返回值是一个布尔值,用于判断 iterable 中的每个元素是否应该被包含在返回的新迭代器对象中。
如果 function(element) 返回 True,则 element 将被包含在返回的迭代器中;
如果 返回 False,则 element 将被过滤掉。
iterable 是一个可迭代对象,例如列表、元组、集合等。
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
def is_even(number):
return number % 2 == 0
even_numbers = filter(is_even, numbers)
print(list(even_numbers)) # 输出 [2, 4, 6, 8, 10]
|
映射map
使用map
| def mul(n):
return n * n
num = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
result = list(map(mul, num)) # 使用map函数对列表num中的每个元素应用mul函数,返回新的列表
print(result) # [1, 4, 9, 16, 25]
|
缓存装饰器
缓存函数的执行结果、并在过期时清除。 以空间换时间
| import time
def auto_expiring_cache(expiration=300):
cache = {}
def decorator(func):
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
# 清除过期缓存
current_time = time.time()
for key, value in list(cache.items()): # 使用list(cache.items())复制缓存条目,以便在循环中删除
if current_time - value['timestamp'] >= expiration:
del cache[key]
# 生成缓存键
key = (func.__name__, str(args),str(kwargs))
print(key)
# 检查缓存中是否已有该键
if key in cache:
return cache[key]['value']
# 调用原始函数
result = func(*args, **kwargs)
# 更新缓存
cache[key] = {
'timestamp': current_time,
'value': result
}
return result
return wrapper
return decorator
@auto_expiring_cache(300)
def ccc(x,y,z):
print(f'计算中...{z}')
return x+y
|
使用生成器
| def iterate(n):
i = 0
while i < n:
yield i
i += 1
for i in iterate(10):
print(i)
|
文件读写
| open()函数详解
r:只读模式
b:以二进制格式
w:只写模式
a:追加模式
+:写模式
read() 函数:逐个字节或者字符读取文件中的内容;
readline() 函数:逐行读取文件中的内容;
readlines() 函数:一次性读取文件中多行内容;
fileinput模块:逐行读取多个文件;
linecache模块:读取文件指定行;
读取大文件:可以借助with...as...上下文管理器;
|
| 模式 |
意义 |
注意事项 |
| r |
只读模式打开文件,读文件内容的指针会放在文件的开头。 |
|
| rb |
以二进制格式、采用只读模式打开文件,读文件内容的指针位于文件的开头,一般用于非文本文件,如图片文件、音频文件等 |
|
| r+ |
打开文件后,既可以从头读取文件内容,也可以从开头向文件中写入新的内容,写入的新内容会覆盖文件中等长度的原有内容 |
操作的文件必须存在 |
| w |
以只写模式打开文件,若该文件存在,打开时会清空文件中原有的内容 |
|
| wb |
以二进制格式、只写模式打开文件,一般用于非文本文件(如音频文件) |
若文件存在,会清空其原有内容(覆 盖文件);反之,则创建新文件 |
| wb+ |
以二进制格式、读写模式打开文件,一般用于非文本文件 |
|
| a |
以追加模式打开一个文件,对文件只有写入权限,如果文件已经存在,文件指针将放在文件的末尾(即新写入内容会位于已有内容之后);反之,则会创建新文件 |
|
| ab |
以二进制格式打开文件,并采用追加模式,对文件只有写权限。如果该文件已存在,文件指针位于文件末尾(新写入文件会位于已有内容之后);反之,则创建新文件 |
|
| a+ |
以读写模式打开文件;如果文件存在,文件指针放在文件的末尾(新写入文件会位于已有内容之后),反之,则创建新文件 |
|
| ab+ |
以二进制模式打开文件,并采用追加模式,对文件具有读写权限,如果文件存在,则文件指针位于文件的末尾(新写入文件会位于已有内容之后);反之,则创建新文件 |
|
| 文件对象提供了 tell() 函数和 seek() 函数。tell() 函数用于判断文件指针当前所处的位置,
而seek() 函数用于移动文件指针到文件的指定位置。该函数的语法格式如下:
file.seek(offset[, whence])
参数释义:
offset:偏移量
whence:指针所在位置,默认为0-开头位置,1表示当前位置,2表示文件尾
# seek()函数设置文件指针位置
f1 = open(file='read.txt', encoding='utf-8')
f1.read(5)
print(f1.tell()) # 指针位置为5
f1.seek(9) # 设置指针位置为9
print(f1.tell()) # 指针位置为9
f1.close()
|
读取大文件(GB)
Python读取文件一般是利用open()函数以及read()函数来完成,但该方式仅适合读取小文件。因为调用read()会一次性读取文件的全部内容,调用readlines()一次读取所有内容并按行返回list。如果文件过大,如10G,会造成MemoryError 内存溢出,正确的做法:可以反复调用read(size)法,每次指定读取size个字节的内容。
处理大文件核心思路:通过参数指定每次读取的大小长度,这样就避免了因为文件太大读取出问题。
线程
| # Threadings
import threading
import time
# 第一个工作函数
def worker1():
for i in range(5):
print("Worker 1: ", i)
time.sleep(1)
# 第二个工作函数
def worker2():
for i in range(15):
print("Worker 2: ", i)
# 创建两个线程
t1 = threading.Thread(target=worker1)
t2 = threading.Thread(target=worker2)
# 启动线程
t1.start()
t2.start()
# 等待线程结束
t1.join()
t2.join()
|
异常处理装饰器
| import traceback
def decorator(func):
# 装饰器方法:用来给函数添加功能,当函数执行失败的时候打印错误信息再抛出异常
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
try:
return func(*args, **kwargs)
except Exception as e:
#打印出错的位置
print(traceback.format_exc())
return wrapper
|
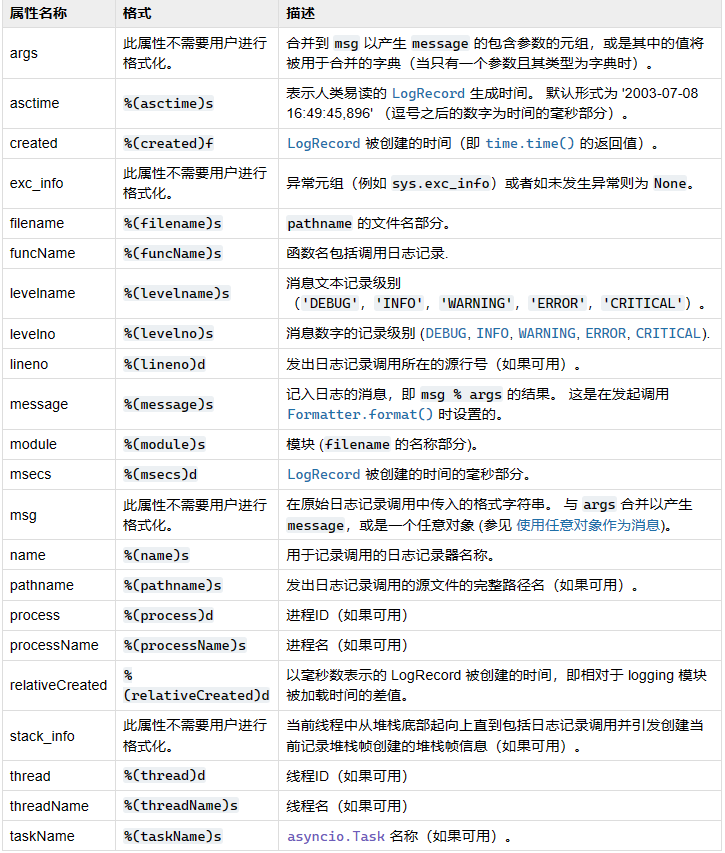
关于logger 日志
https://docs.python.org/zh-cn/3/library/logging.html#logrecord-attributes
https://docs.python.org/zh-cn/3/library/logging.html#logging.Handler 自定义处理器可以集成 这个类
| 自定义消息格式,记录日志的文件
logging.basicConfig(format='%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s',filename='example.log', encoding='utf-8', level=logging.WARNING)
logging.basicConfig(format='%(asctime)s %(funcName)s%(lineno)d - %(levelname)s - %(message)s',datefmt='%H:%M:%S')
import logging
from logging.config import fileConfig
conf = fileConfig("logging.conf")
下方是配置文件 logging.conf
[loggers]
keys=root,simpleExample
[handlers]
keys=consoleHandler
[formatters]
keys=simpleFormatter
[logger_root]
level=DEBUG
handlers=consoleHandler
[logger_simpleExample]
level=DEBUG
handlers=consoleHandler
qualname=simpleExample
propagate=0
[handler_consoleHandler]
class=StreamHandler
level=DEBUG
formatter=simpleFormatter
args=(sys.stdout,)
[formatter_simpleFormatter]
format=%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s
|